


Generation of Mobile networks
Edited By mpm | Updated: 2024-11-19 18:11:58
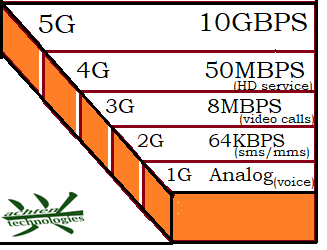
Generation of Mobile networks
|
Generations |
Technology |
Features |
Advantages/ Drawbacks |
|
1G (1st Generation) ` |
Frequency Bands: 800 MHz /Data Speed: Up to 2.4 Kbps |
voice communication |
No data services./ Poor voice quality and security. Large, bulky phones. |
|
2G (2nd Generation)
|
Digital (GSM, CDMA) Digital signals // Frequency Bands: 900 MHz, 1800 MHz Data Speed: Up to 64 Kbps |
Better voice quality SMS and MMS. . |
Basic data services, Better battery life and smaller phones |
|
3G (3rd Generation)
|
UMTS, CDMA2000/ Frequency Bands: 2100 MHz/ Data Speed: Up to 2 Mbps (theoretically up to 21.6 Mbps with HSPA+) |
Higher speed data service / mobile internet, video calls, and mobile TV. |
Improved voice quality and capacity |
|
4G (4th Generation)
|
LTE, WiMAX Frequency Bands: 700 MHz to 2.6 GHz Data Speed: Up to 1 Gbps (theoretically), Multiple Input Multiple Output & Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing. |
Support for high-definition mobile TV, video conferencing, and cloud. |
Significant increase in data speeds and capacity. Lower latency and improved spectral efficiency. Lower latency and improved spectral efficiency
|
|
5G (5th Generation)
|
NR (New Radio) Frequency Bands: There are 3 types of 5G wireless bands :-LOW: frequencies between 600 and 900 MHz),MID: between 1 and 6 GHz HIGH BAND :Transmits from 24 to 47 GHz. Data Speed: Up to 20 Gbps (theoretically) |
Ultra-high data speeds and very low latency. Support for massive IoT (Internet of Things) and critical communications.
|
Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), and massive machine-type communication (mMTC). Network slicing for customized network services. Improved energy efficiency and capacity. |